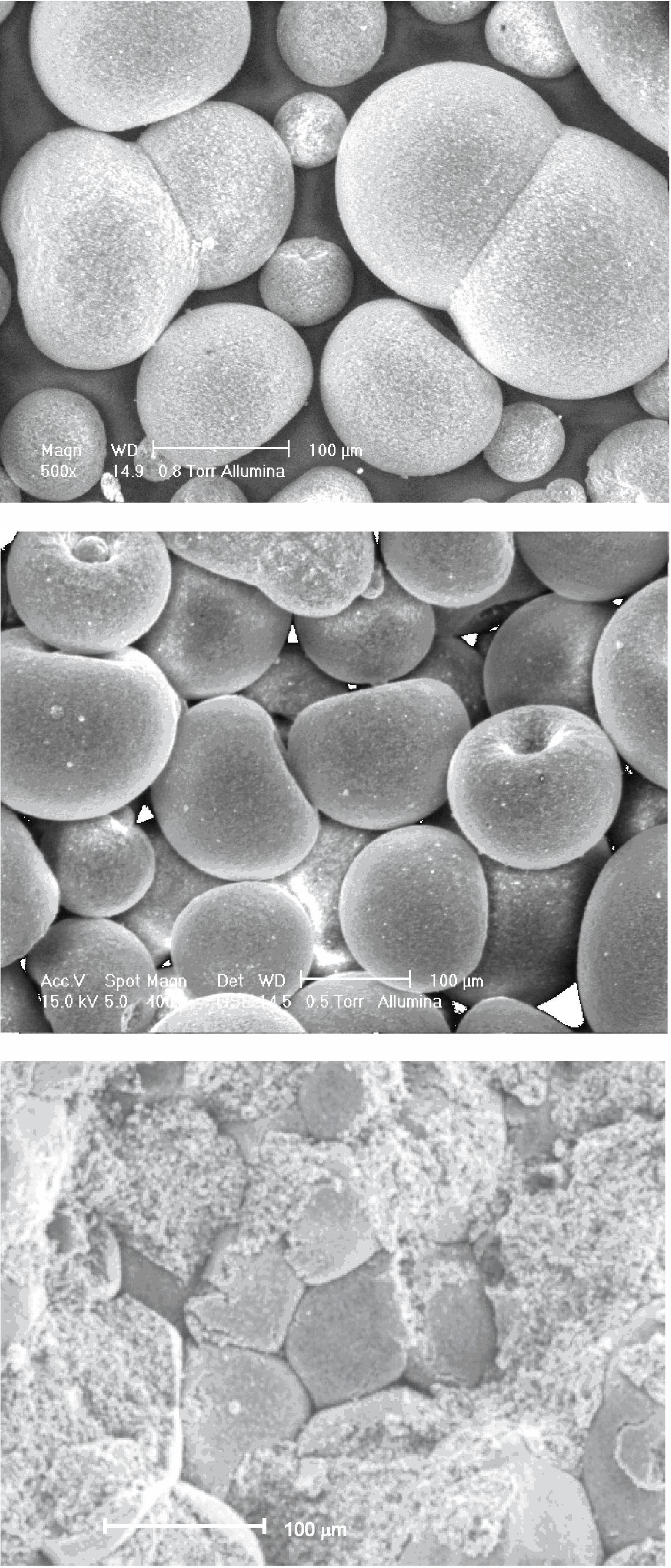
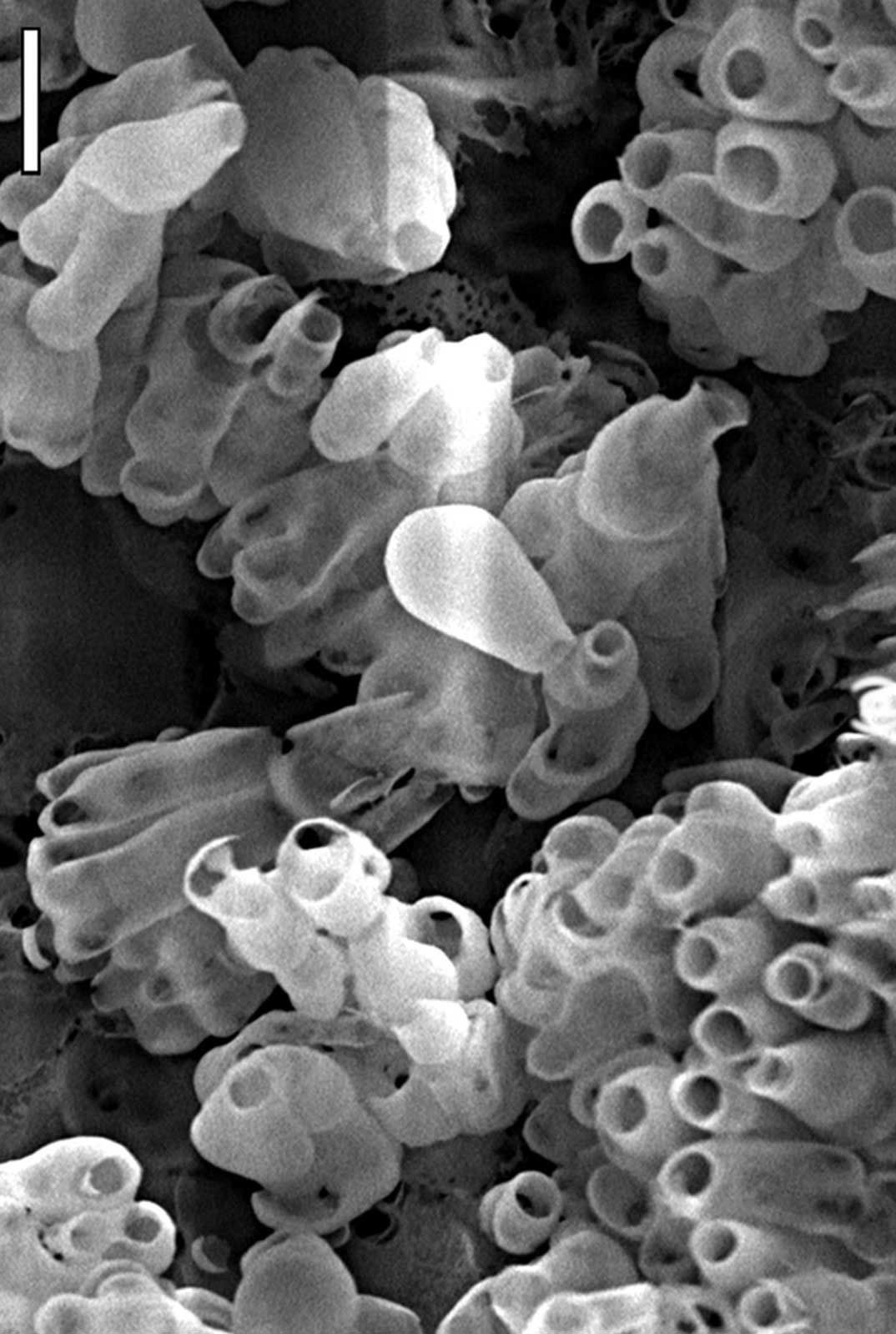
Technical ceramics materials (e.g. Alumina ceramics, Mullite, Silicon Carbide, Zirconia, Porous Electrofused Silica, Boron Nitride, Alumina Titanate)
Overview
Our principal materials are:
ALUMINA
Aluminium oxide (Al2O3) provides the basis for one of the most important technical oxide ceramic material groups. Alumina ceramics materials have established themselves as the material of choice for a wide range of applications as modern technologies demand improved performance in order to push products and processes to greater limits. Densely sintered alumina ceramics are characterised by:-
- high strength and hardness,
- temperature stability,
- Electrical insulation,
- high wear and friction resistance
- corrosion resistance even at high temperatures.
Industrial alumina ceramics parts made from alumina oxide are usually composed of alumina with additions of other materials such as silica or magnesia. Alumina ceramics contents tend to range from 72% up to 99.99% alumina for some applications. Higher alumina contents are generally used where the application demands a higher performance in terms of temperature or wear capability.
A range of high purity alumina ceramics materials for use in high temperature, wear, corrosive or electrical insulation applications are available from Anderman Industrial Ceramics and its partner network. Stock is available in rods, tubes, thermocouple protection tubes, plates, crucibles, insulators. Special alumina ceramics shapes also available on request according to specific and discreet customer demands.
- EA999 – Alumina 99.9% content
- EA998 – Alumina 99.8% content
- EA995 – Alumina 99.5% content
- EA96 – Alumina 96% content
- EA95 – Alumina 95% content
- EA99P – Alumina – 99% Porous
- EAZ20 – Zirconia Toughened Alumina ZTA
MULLITE
Mullite is a material that is manufactured by combining Alumina with Silica, fused together during sintering, in various combinations to produce a family of materials. Known as Mullite for the dense materials and Porous mullite or corundum for the porous grades.
Synthetic Mullite (Al2O3–SiO2) products are available in both impervious and porous forms. Densely sintered (impervious) mullite combines high strength with good thermal shock resistance. Porous mullite have a reasonably high strength combined with low thermal expansion giving improved levels of thermal shock.
Mullite ceramics with high thermal shock and operating temperatures up to 2910F (1600C) are used in furnaces, heaters, electrical insulation, wear and corrosion resistant applications. Stock is available in rods, Mullite tubes, insulators, thermocouple protection sheaths and crucibles.
These mullite materials are also available in Special and custom shapes according to specific and discreet customer demands.
- EM60 – Mullite – Impervious – 60% (min) alumina content
- EM60P – Mullite (sillimanite) – Porous – 60% alumina content
- EM80P – Corundum – Porous – 80% alumina content
STEATITE
 Steatite is a ceramic material based on natural raw materials. It consists of soapstone (Mg(Si4O10)(OH)2), which is also the main component, a natural Magnesium silicate with additions of clay and feldspar or Barium carbonate.
Steatite is a ceramic material based on natural raw materials. It consists of soapstone (Mg(Si4O10)(OH)2), which is also the main component, a natural Magnesium silicate with additions of clay and feldspar or Barium carbonate.
Steatite ceramic is suitable for metal/ceramic component solutions and even for applications that require reduced permittivity. High-strength, vacuum-sealed metal-ceramic solder joints between fusible alloys and Steatite ceramics can be produced. This results in higher thermal shock resistance at high pressure but also increased transparency to microwave frequencies.
Steatite material exhibits low contraction during firing. This allows production of components to precise tolerances. Both small and highly detailed shapes can be achieved using cost efficient production methods, making steatite suitable for volume manufacture of insulating components.
Steatite impresses with its very good dielectric strength, ageing resistance, UV radiation resistance, high mechanical strength, a temperature resistance and dimensional stability up to 1000°C. In addition, there is the tracking resistance and it is non-flammable.
Typical applications for Steatite ceramics include, but not limited to; bushings, electric heating elements, igniters, lamp bases/sockets, resistors, stand offs, band heaters, knife sharpeners, thermocouple cores, thermostat pins, load banks, ovens, furnaces, connectors, spacers, electrostatic air cleaners, relays, switches, fuses, substrates, sensors and stiffening rods.
Anderman’s offerings include both a glazed and non-glazed Steatite. Glazing Steatite provides improved electrical resistance, whilst providing an impervious protective surface.
TECHNICAL CERAMICS
In addition to the principal materials listed above we are also able to offer a number of special technical ceramic materials for a range of high temperature, wear and electrical resistance applications.
REQUEST A DATA SHEET ON MATERIALS BELOW
- Steatite
- Lava
- Quartz
- Forsterite
- Yttria
- Magnesia
Our range of ceramic materials is considerable and our experience enables us to source other, more specialist materials, upon request. We can deliver to most dimensional requests and also hold considerable stocks of standard shapes and sizes.
With our manufacturing partners we have over 100 years experience in ceramic forming technology utilising processes such as extrusion, slip casting, injection moulding, isostatic pressing and uniaxial pressing.
CLICK HERE FOR STANDARD PRODUCT LIST
QUARTZ
Quartz (Fused Quartz) as an industrial raw material is used to make various refractory shapes such as crucibles, trays, shrouds and rollers for several high temperature thermal processes including steelmaking, investment casting and glass manufacture. Refractory shapes made from Quartz have excellent thermal shock resistance and are chemically inert to most components and compounds including almost all acids, regardless of the application. Translucent fused silica (quartz) tubes are normally used to replace electric elements in room heaters, industrial furnaces and other similar applications. Quartz, in all its forms, offers a diversity of properties such as:
- Extreme Hardness
- Very Low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
- Resistance to High Temperature
- High Chemical Purity
- High Corrosion Resistance
- Extensive Optical Transmission from Ultra-Violet to Infra-Red
- Excellent Electrical Insulation Qualities
- Remarkable Stability Under Atomic Bombardment
Our range of quartz products shows a very wide variety of possibilities, from small laboratory equipment to large wafer carriers or large diameter tubes.
SILICON CARBIDE
Porous silicon carbides with excellent thermal shock, high strength and high temperature operating capability up to 2910 F (1600C). Excellent for use in furnaces and molten metal applications due to it’s non wetting properties. Stock available in tubes, thermocouple sheaths, rods, crucibles and beams.
- EC70P – Silicon Carbide 70% (mullite bonded)
- EC90P – Silicon Carbide 90% (mullite bonded)
- EC100P – Recrystallised Silicon Carbide
ZIRCONIA
A range of zirconia materials either dense or with porosity. These materials offer high temperature capability upto 4370F (2400C) as well as excellent performance in areas of high wear and corrosion. Products are available as tubes, rods, Zirconia crucibles and a wide range of other shapes.
- EZY94 – Yttria partially stabilised
- EZY88 – Yttria fully stabilised
- EZM96 – Magnesia partially stabilised
- EZC96P – Calcia fully stabilised
- EZZ66P – Zircon
POROUS ELECTROFUSED SILICA
An improved solution for high thermal shock applications involving rapid heat and cooling temperature cycles
Anderman Ceramics is pleased to offer its porous electrofused silica ES99P grade of material. This combines a maximum operating temperature of 1680°C with excellent thermal shock resistance for rapid heating and cooling needs. This combination is extremely beneficial in thermal applications beyond 1200°C where contact with molten materials (metal or glass) produces severe thermal shock in the ceramic body needed to contain the molten liquid.
Our extensive range of manufacturing capabilities ensures that shapes can be manufacturing to exacting dimensional control as well as a large range of sizes, from a few cm to many metres in size.
Anderman Industrial Ceramics specialise in all aspects of the supply of ceramic and refractory products for metals, chemical, cement and glass production. Our products are used throughout industrial production process chains wherever heat, wear or corrosion is involved
Advantages:
- Minimal contamination of metal or glass
- High thermal insulation
- Reduced inclusions in metal
- Excellent thermal shock properties
- No preheating needed
- High purity
Applications:
- Casting for non-ferrous metals
- Control of metal flow
- Float glass manufacturing
- Steel strip rolling
Porous Electrofused Silica – ES99P
BORON NITRIDE
 Hexagonal Boron Nitride has a microstructure similar to that of Graphite. In both materials, this structure, made up of layers of tiny platelets, is responsible for excellent machinability and low-friction properties. We refer to this as hexagonal boron nitride (HBN) or white graphite.
Hexagonal Boron Nitride has a microstructure similar to that of Graphite. In both materials, this structure, made up of layers of tiny platelets, is responsible for excellent machinability and low-friction properties. We refer to this as hexagonal boron nitride (HBN) or white graphite.
Boron Nitride has excellent electrical insulation and thermal conductivity which make the material very useful as a heat sink in high-power electronic applications. Its properties compare favourably with beryllium oxide, aluminium oxide, and other electronic packaging materials, and are easier to machine to defined shapes and sizes, making it a preferred material to produce custom-made parts within a thermal management application.
Boron Nitride (BN) is typically hot pressed into blocks and then machined to finished requirements. Compared with many ceramic materials BN is relatively easy to machine, making it an ideal material for low to medium volume production.
Temperature stability and excellent resistance to thermal shock make BN the ideal material in the toughest high-temperature environments such as equipment for plasma arc welding, diffusion source wafers, and semiconductor crystal-growth equipment and processing.
BN is inorganic, inert, non-reactive with halide salts and reagents, and is non-wetting when used in a molten-metal application. These characteristics, combined with low thermal expansion, make it ideal for interface materials used in various molten metal processes.
ALUMINA TITANATE
 Anderman Industrial Ceramics offer reaction sintered aluminium titanate, which is a material most commonly used in non-ferrous metal melting. It has also found applications in iron and steel, chemical and medical sectors.
Anderman Industrial Ceramics offer reaction sintered aluminium titanate, which is a material most commonly used in non-ferrous metal melting. It has also found applications in iron and steel, chemical and medical sectors.
The majority of our supply to date is aluminium titanate formed parts to non-Ferrous cast houses and foundries. The extraordinary properties of Alumina Titanate include high thermal shock resistance, low thermal conductivity and exceptional non-wettability to most Non-ferrous molten metal.
These properties are achieved by combining high purity alumina and titania in a precision controlled reaction sintering process. This enables us to engineer a micro-porous microstructure provides the benefits as seen in application including a longer service life and negates the need for any pre-heating as it is able to be exposed directly to molten metal.
Our valued customers have referenced our Alumina Titanate material offers them increased process reliability, reducing the risk of metal freeze-offs and Improving production yields when compared to alternative material options.
Other significant benefits in addition to increased service life are the non-contamination of the melt improving product quality and plant efficiency.
Dosing tubes up to 200mm in diameter and 590mm in length, riser tubes used in low pressure die casting, spouts, retainer rings, pouring nozzles, thimbles for billet casting as a technology advancement of historically used fused silica thimbles are all parts Anderman are regularly supplying.
RARE EARTH MATERIALS
Rare earth refractory oxide ceramics exhibiting very high thermal stability, wear resistance and strength. Widely used in applications above 3090F (1700C), nuclear, high performance metal melting, oxygen sensors and semiconductor applications. Products are offered in a wide range of shapes including crucibles, ceramic tubes, laboratory furniture and thermocouple sheaths.
- EREY99 – Yttrium Oxide
- EREH99 – Hafnium Oxide – high purity
- EREH97Y – Hafnium Oxide stabilized with yttrium oxide
- EREC99 – Cerium Oxide
REFRACTORY MATERIALS
In addition to the principle materials listed above Anderman also offers a range of specialty refractory materials for high temperature applications.
REQUEST A DATA SHEET ON MATERIALS BELOW
- Cordierite
- Alumina Titanate
- Fused Silica
- Sillimanite
- Corundum
Alumina
Mullite
Steatite
STEATITE
 Steatite is a ceramic material based on natural raw materials. It consists of soapstone (Mg(Si4O10)(OH)2), which is also the main component, a natural Magnesium silicate with additions of clay and feldspar or Barium carbonate.
Steatite is a ceramic material based on natural raw materials. It consists of soapstone (Mg(Si4O10)(OH)2), which is also the main component, a natural Magnesium silicate with additions of clay and feldspar or Barium carbonate.
Steatite ceramic is suitable for metal/ceramic component solutions and even for applications that require reduced permittivity. High-strength, vacuum-sealed metal-ceramic solder joints between fusible alloys and Steatite ceramics can be produced. This results in higher thermal shock resistance at high pressure but also increased transparency to microwave frequencies.
Steatite material exhibits low contraction during firing. This allows production of components to precise tolerances. Both small and highly detailed shapes can be achieved using cost efficient production methods, making steatite suitable for volume manufacture of insulating components.
Steatite impresses with its very good dielectric strength, ageing resistance, UV radiation resistance, high mechanical strength, a temperature resistance and dimensional stability up to 1000°C. In addition, there is the tracking resistance and it is non-flammable.
Typical applications for Steatite ceramics include, but not limited to; bushings, electric heating elements, igniters, lamp bases/sockets, resistors, stand offs, band heaters, knife sharpeners, thermocouple cores, thermostat pins, load banks, ovens, furnaces, connectors, spacers, electrostatic air cleaners, relays, switches, fuses, substrates, sensors and stiffening rods.
Anderman’s offerings include both a glazed and non-glazed Steatite. Glazing Steatite provides improved electrical resistance, whilst providing an impervious protective surface.
Zirconia
Refractories
- High Alumina
- Cordierite
- Sillimanite
- Corundum
Porous Electrofused Silica
Boron Nitride
Other
- Quartz
- Forsterite
- Steatite
- Lava
- Yttria
- Magnesia